Pay Per Click (PPC) helps you place your brand directly in front of potential customers almost instantly—without having to wait a few months for SEO efforts to gain momentum. Yet, jumping in without a solid strategy is like throwing your marketing budget into a black hole.
That’s why establishing a robust PPC foundation is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through each step of building a strategy that’s not only practical and effective, but adaptable to your unique business goals. Whether you’re managing campaigns internally or considering partnering with a specialized agency like Straight North, this roadmap will provide the clarity you need to make intelligent, data-driven advertising decisions.
Understanding the Fundamentals of PPC
PPC is a digital advertising model that allows businesses to place ads on search engines, social media platforms, and other websites. These ads are seen prominently by users who search on the platform. Businesses only pay when users click on those ads. Unlike traditional advertising methods where you pay upfront for ad placement regardless of results, PPC operates on a performance-based system—you only invest when someone clicks through to your website. This makes PPC one of the most measurable and cost-effective forms of digital marketing, as every dollar spent can be directly tied to user engagement and, ultimately, business results.
Think of PPC as securing premium real estate on search engines and social platforms. By employing PPC you are essentially buying visibility when potential customers are searching for your product or service.
The major players in the PPC landscape include:
- Google Ads: The undisputed leader for search campaigns, commanding over 90% of search market share.
- Microsoft Advertising (Bing): Often overlooked but frequently delivers lower competition and reduced cost-per-clicks. For example, Bing consists of nearly 30% of desktop computer search traffic in the United States.
- Social platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram, and TikTok: Ideal for targeting audiences based on detailed demographics, interests, and behaviors.
- Amazon Advertising: Essential for e-commerce brands selling on the platform.
- YouTube Ads: Perfect for video-first marketing strategies.
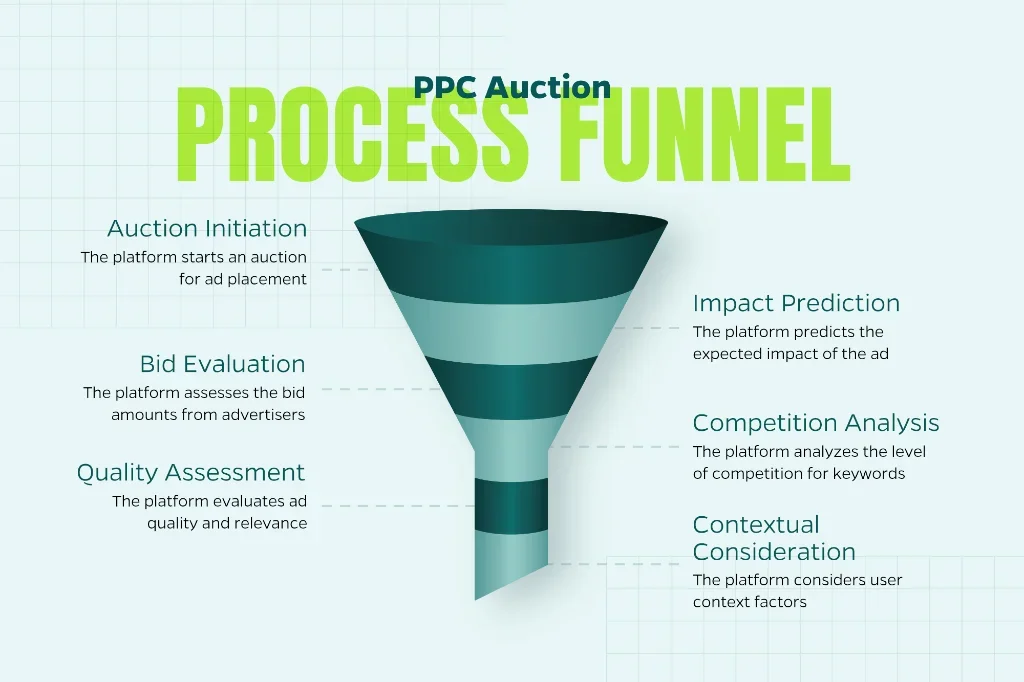
The PPC Auction System Explained
Understanding how PPC works behind the scenes can dramatically improve your results. Every time someone performs a search, platforms conduct a lightning-fast auction (within milliseconds). Your ad’s placement and visibility depend on several critical factors:
- Your bid amount: What you’re willing to invest per click.
- Ad quality and relevance: How closely your message aligns with the searcher’s intent.
- Expected impact: Historical click-through rates, ad extensions, and landing page experience.
- Competition level: How many other advertisers are targeting the same keywords.
- User context: Device, location, time of day, and search history.
Unlike traditional advertising where you pay for impressions regardless of engagement, PPC ensures you’re investing in measurable actions. This performance-based model makes it easier to calculate ROI and justify marketing spend.
Essential Metrics Every PPC Advertiser Should Master
Before diving deeper into strategy, let’s establish the key performance indicators that will guide your decision-making:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of impressions that result in clicks. Industry benchmarks vary, but 6-7% represents solid performance for search campaigns, while display ads typically see 0.5-1%.
- Cost Per Click (CPC): The actual amount you pay for each click. This varies dramatically by industry—e-commerce might see $1.16 average CPCs, while competitive sectors like legal services can reach $6.40 or higher.
- Conversion Rate (CVR): The percentage of clicks that lead to your desired action, whether that’s a purchase, form submission, or phone call.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): How much you spend to acquire one customer or lead.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Revenue generated for every dollar invested. A 4:1 ratio serves as a healthy baseline, though this varies significantly by business model.
- Quality Score: Google’s 1-10 rating of your ad relevance, expected CTR, and landing page experience.
- Impression Share: The percentage of available impressions your ads received.
The appeal of PPC lies in its unique combination of speed and precision. While SEO builds long-term organic authority and email marketing nurtures existing relationships, PPC serves as your express lane to visibility and customer acquisition—provided you manage it strategically.
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Objectives
Every successful PPC strategy begins with absolute clarity about what you want to achieve. Vague objectives like “get more traffic” or “increase brand awareness” won’t cut it—you need goals that follow the SMART framework: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Examples of Well-Defined PPC Goals
- Lead Generation: “Generate 75 qualified B2B leads per month within four months, maintaining a cost per acquisition under $65.”
- E-commerce Sales: “Achieve a 6:1 ROAS on product campaigns during Q4, with at least $50,000 in attributed revenue.”
- Local Business Growth: “Increase store visits by 40% over six months while keeping cost per store visit under $12.”
- SaaS Growth: “Drive 200 free trial signups monthly with a trial-to-paid conversion rate of at least 25%.”
Aligning PPC Goals with Business Priorities
Your PPC objectives should directly support broader business goals. Consider these common scenarios:
- Startups often prioritize lead generation and brand awareness to build market presence.
- E-commerce businesses typically focus on sales volume, ROAS, and customer lifetime value.
- B2B companies usually emphasize lead quality, sales-qualified leads, and pipeline contribution.
- Local services concentrate on phone calls, appointment bookings, and geographic reach.
- SaaS companies balance trial signups, demo requests, and customer acquisition costs.
Understanding what success looks like will influence every subsequent decision in your PPC strategy, from platform selection to budget allocation.
Step 2: Conduct Comprehensive Keyword Research
Keywords form the foundation of successful PPC campaigns—they’re the bridge connecting what people search for with what your business offers. If you choose your keywords poorly, you’ll burn through your budget by attracting visitors who have no intention of converting.
Understanding Keyword Match Types
- Broad Match: Provides maximum reach but often attracts irrelevant traffic. Use sparingly and monitor closely.
- Phrase Match: Offers moderate control while maintaining reasonable reach. Your keyword must appear in the user’s search, but additional words can appear before or after.
- Exact Match: Delivers the highest intent and control but offers limited reach. This approach is ideal for high-converting, well-tested keywords.
- Negative Keywords: You can also exclude irrelevant searches that waste your budget. For example, you probably want to add “free” as a negative if you’re selling premium products.

Advanced Keyword Research Strategies
Beyond basic keyword identification, consider these sophisticated approaches:
Competitor Intelligence: Use tools like SEMrush or SpyFu to analyze competitor ad copy, keywords, and landing pages. Look for gaps in your competitors’ strategy that you can exploit.
Search Query Mining: Regularly review search term reports to discover new keyword opportunities and negative keyword additions. Users often search in ways you wouldn’t expect.
Seasonal Keyword Planning: Many industries experience predictable seasonal fluctuations. Plan campaigns around holidays, industry events, or cyclical demand patterns.
Long-Tail Keyword Focus: Phrases like “best noise-cancelling headphones for frequent travelers under $200” convert exceptionally well because they indicate high purchase intent and face less competition.
Essential Keyword Research Tools
- Google Keyword Planner: Free tool providing search volume estimates and CPC ranges.
- Microsoft Keyword Planner: Often reveals lower competition opportunities on Bing.
- SEMrush/Ahrefs/BrightEdge: Premium tools offering competitive intelligence and deeper market insights.
- Answer the Public: Excellent for discovering question-based keywords.
- Google Search Console: Reveals which organic keywords drive traffic to your site. You can adapt many of these keywords for PPC.
Step 3: Craft Compelling Ad Creatives
Up to this point, we offered some details on PPC strategy. Yet, there is another important component: creative. The advertisement you create often represents the first interaction potential customers have with your brand. This initial impression can determine whether they click through to learn more or scroll past to a competitor. Let’s look at some best practices for your ads and creative.
Search Ad Structure and Best Practices
Headlines (30 characters each):
- Lead with your primary keyword for relevance.
- Emphasize unique value propositions.
- Include emotional triggers like urgency or social proof.
- Example: “Premium Wireless Headphones | Free 2-Day Shipping | 5-Star Reviews.”
Descriptions (90 characters each):
- Expand on benefits rather than just features.
- Include compelling calls-to-action.
- Address potential objections or concerns.
- Highlight special offers or guarantees.
Ad Extensions:
- Sitelinks: Direct users to specific pages (pricing, testimonials, contact).
- Callout Extensions: Highlight key benefits like “24/7 Support” or “Money-Back Guarantee.”
- Structured Snippets: Showcase product categories or service types.
- Location Extensions: Essential for local businesses.
- Call Extensions: Enable direct calling from mobile devices.
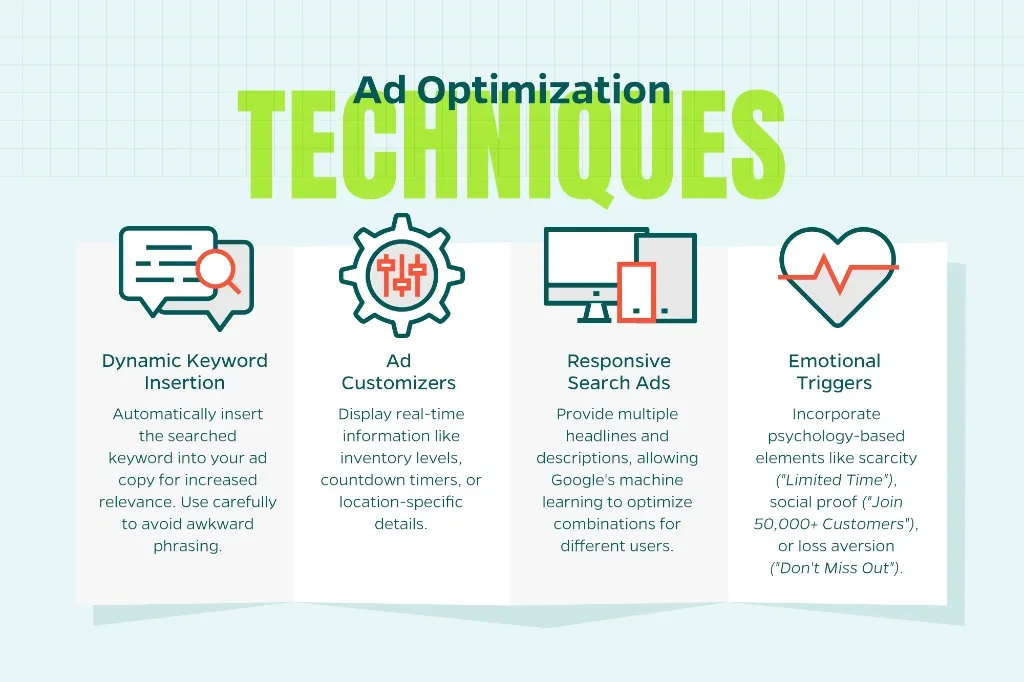
Advanced Ad Creative Strategies
Dynamic Keyword Insertion: Automatically insert the searched keyword into your ad copy for increased relevance. Use carefully to avoid awkward phrasing.
Ad Customizers: Display real-time information like inventory levels, countdown timers, or location-specific details.
Responsive Search Ads: Provide multiple headlines and descriptions, allowing Google’s machine learning to optimize combinations for different users.
Emotional Triggers: Incorporate psychology-based elements like scarcity (“Limited Time”), social proof (“Join 50,000+ Customers”), or loss aversion (“Don’t Miss Out”).
Display and Video Ad Considerations
For visual campaigns, focus on:
- Professional, high-quality imagery that reflects your brand.
- Clear, readable text that works across different screen sizes.
- Strong branding elements including logos and consistent color schemes.
- Compelling calls-to-action that stand out visually.
- Mobile optimization since most display traffic comes from mobile devices.
Step 4: Master Targeting and Segmentation
PPC’s greatest strength lies in its precision targeting capabilities. Instead of broadcasting messages to everyone, you can focus on people most likely to become customers.
Core Targeting Options
Demographic Targeting:
- Age ranges based on your ideal customer profile.
- Gender preferences when relevant to your product.
- Household income levels for premium or budget-focused offerings.
- Parental status for family-oriented products.
Geographic Targeting:
- Radius targeting around physical locations.
- ZIP code or city-specific campaigns.
- State or region-level targeting for broader reach.
- International targeting with language considerations.
Device and Platform Targeting:
- Mobile vs. desktop performance often varies significantly.
- Tablet users frequently exhibit different browsing behaviors.
- Operating system targeting for app-focused campaigns.
Advanced Targeting Strategies
Audience Remarketing: Re-engage website visitors who didn’t convert initially. These campaigns often achieve 50-100% higher conversion rates than cold traffic campaigns.
Similar Audiences/Lookalikes: Platforms can identify users who share characteristics with your best customers.
In-Market Audiences: Target users actively researching products or services like yours.
Custom Intent Audiences: Build audiences based on specific URLs visited or apps used.
Life Event Targeting: Reach people during significant life moments like moving, getting married, or starting new jobs.
Dayparting: Adjust bids based on when your audience is most active or when conversions peak.
Step 5: Develop Smart Budgeting and Bidding Strategies
Effective budget management separates successful PPC campaigns from expensive learning experiences.
Budget Planning Framework
Testing Phase:
- Allows for meaningful data collection.
- Enables testing of multiple ad variations.
- Provides insights into performance patterns.
- Typically requires 2-4 weeks for statistical significance.
Scaling Phase (Based on proven ROI):
- Increase budgets on highest-performing campaigns.
- Maintain testing budgets for new opportunities.
- Consider seasonal adjustments and market changes.
Bidding Strategy Evolution
Manual CPC (Beginners):
- Provides complete control over individual keyword bids.
- Ideal for learning campaign dynamics.
- Requires more time investment but offers valuable insights.
- Best for campaigns with limited historical data.
Enhanced CPC (Intermediate):
- Automatically adjusts manual bids based on conversion likelihood.
- Provides a bridge between manual and automated bidding.
- Maintains some control while leveraging machine learning.
Smart Bidding (Advanced):
- Target CPA: Automatically sets bids to achieve your desired cost per acquisition.
- Target ROAS: Optimizes bids to hit specific return on ad spend goals.
- Maximize Conversions: Focuses on generating the most conversions within budget.
- Maximize Conversion Value: Prioritizes high-value conversions.
Budget Allocation Best Practices
- Start conservative: Better to begin with smaller budgets and scale up based on performance.
- Monitor daily: Budget can be consumed quickly in competitive markets.
- Plan for seasonality: Adjust budgets for holidays, industry events, or cyclical demand.
- Diversify across campaigns: Don’t put all budget into one campaign or keyword theme.
- Reserve testing budget: Allocate 10-20% of budget for testing new opportunities.
Step 6: Optimize Landing Pages for Maximum Conversions
A click represents just the beginning of the conversion process. Your landing page must deliver on the promise made in your ad while guiding visitors toward your desired action.
Conversion-Focused Landing Page Elements
Message Match:
- Headline should directly connect to your ad copy.
- Visual elements should reinforce the ad’s promise.
- Maintain consistent terminology and value propositions.
Page Load Speed:
- Aim for under 3 seconds on all devices.
- Optimize images without sacrificing quality.
- Minimize redirects and unnecessary plugins.
- Use content delivery networks (CDNs) for faster loading.
Mobile Optimization:
- Over 60% of PPC traffic typically comes from mobile devices.
- Ensure buttons are easily clickable on touchscreens.
- Simplify forms for mobile completion.
- Test thoroughly across different devices and browsers.
Trust and Credibility Signals:
- Customer testimonials and reviews.
- Security badges and certifications.
- Money-back guarantees or return policies.
- Professional design and error-free copy.
- Contact information and business address.
Advanced Landing Page Optimization
Form Optimization:
- Minimize required fields to reduce friction.
- Use multi-step forms for longer submissions.
- Implement smart defaults and auto complete.
- A/B test form placement and design.
Call-to-Action Optimization:
- Use action-oriented language (“Get Started” or “Claim Your Discount”).
- Make buttons visually prominent with contrasting colors.
- Test button placement, size, and wording.
- Consider multiple CTAs for different stages of the buyer journey.
Social Proof Integration:
- Display customer logos or testimonials prominently.
- Show real-time user activity (“5 people signed up in the last hour”).
- Include specific, credible statistics and results.
- Feature press mentions or industry awards.
Step 7: Implement Comprehensive Tracking and Analytics
Without proper measurement, PPC becomes expensive guesswork. Establishing robust tracking from day one ensures you can make data-driven optimization decisions.
Essential Tracking Setup
Google Analytics 4 and Google Tag Manager:
- Set up conversion tracking for all desired actions.
- Implement enhanced e-commerce tracking for online stores.
- Configure goal funnels to identify drop-off points.
- Connect Google Ads for seamless data sharing.
Platform-Specific Tracking:
- Facebook Pixel for Meta advertising platforms.
- LinkedIn Insight Tag for B2B campaigns.
- Microsoft UET Tag for Bing Ads.
- Platform-specific conversion tracking for accurate attribution.
Call Tracking Solutions:
- Essential for service-based businesses.
- Provides insights into offline conversions.
- Enables keyword-level call attribution.
- Helps optimize campaigns for phone lead generation.
Advanced Analytics and Optimization
Attribution Modeling:
- Understand the customer journey across multiple touchpoints.
- Avoid over-crediting last-click interactions.
- Consider first-click, linear, or data-driven attribution models.
- Adjust based on your typical sales cycle length.
Regular Performance Reviews:
- Weekly: Review basic metrics, pause underperforming ads, adjust bids.
- Monthly: Analyze trends, update negative keywords, review audience performance.
- Quarterly: Evaluate overall strategy, test new platforms or campaign types, assess budget allocation.
Competitive Intelligence:
- Use Auction Insights reports to understand competitor activity.
- Monitor competitor ad copy and landing page changes.
- Identify opportunities when competitors reduce activity.
- Adjust strategies based on competitive landscape shifts.
Common Mistakes That Drain PPC Budgets
Even experienced advertisers can make a costly mistake. Learning to recognize and avoid them can save thousands in wasted spend:
Strategic Mistakes
Launching Without Clear Goals: Campaigns need specific, measurable objectives tied to business outcomes. Define success metrics before spending a dollar.
Ignoring Negative Keywords: This oversight wastes more budget than almost any other mistake. Regularly review search term reports and build comprehensive negative keyword lists. A software company selling premium tools should exclude “free,” “cheap,” and “DIY” to avoid unqualified clicks.
Overlooking Mobile Experience: With mobile traffic dominating most industries, a poor mobile experience destroys ROI. Ensure landing pages load quickly, forms are easy to complete, and phone numbers are clickable.

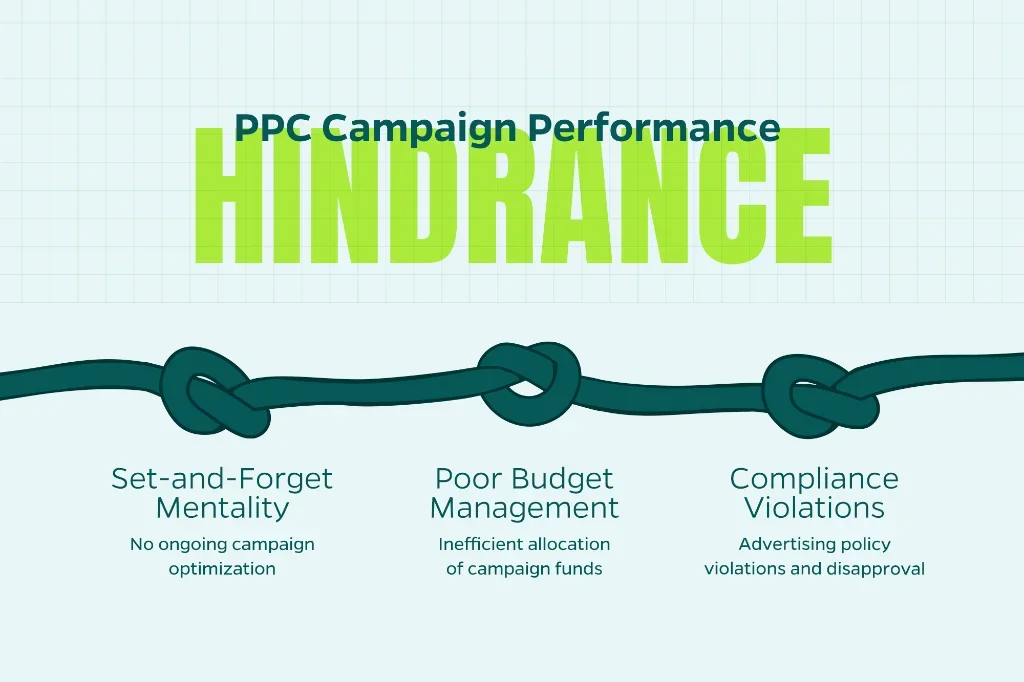
Tactical Mistakes
Set-and-Forget Mentality: PPC requires ongoing optimization. Market conditions change, competitors adjust strategies, and new opportunities emerge constantly. Schedule weekly optimization sessions and monthly strategic reviews.
Poor Budget Management: Overspending on underperforming campaigns while underfunding profitable ones. Monitor daily spend and reallocate budgets based on performance data, not gut feelings.
Compliance Violations: Platforms like Google and Facebook enforce strict advertising policies. Claims like “guaranteed results” or “#1 in the world” risk ad disapproval or account suspension. Keep messaging honest, specific, and compliant with platform guidelines.
Measurement Mistakes
Tracking Only Vanity Metrics: Impressions and clicks don’t pay the bills. Focus on conversion rates, cost per acquisition, and return on ad spend. These metrics directly connect to business profitability.
Attribution Errors: Failing to track the complete customer journey leads to poor budget decisions. B2B buyers often research for weeks before converting, while impulse purchases might happen immediately. Understand your sales cycle and set up appropriate tracking.
Advanced PPC Strategies for 2025
As PPC platforms evolve, staying ahead of trends can provide significant competitive advantages:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Smart Bidding Adoption: Platforms increasingly favor automated bidding strategies. Start with Target CPA or Target ROAS once you have sufficient conversion data (typically 15-20 conversions per month).
Responsive Ad Formats: Provide multiple headlines and descriptions, allowing AI to test combinations and optimize for different users and contexts.
Predictive Audiences: Platforms can now identify users likely to convert before they even search for your products, expanding reach beyond traditional keyword-based targeting.
Privacy and Data Changes
First-Party Data Strategy: With third-party cookies disappearing, building and utilizing first-party data becomes crucial. Implement customer match campaigns using email lists and phone numbers.
Contextual Targeting: As behavioral tracking decreases, contextual advertising (placing ads based on page content rather than user behavior) gains importance.
Server-Side Tracking: Implement server-side conversion tracking to maintain accuracy despite browser privacy restrictions.
Emerging Platform Opportunities
Connected TV Advertising: As streaming services grow, CTV provides new opportunities for video-focused campaigns with precise targeting capabilities.
Voice Search Optimization: Optimize for conversational, question-based queries as voice search adoption increases.
Visual Search Campaigns: Platforms continue expanding visual search capabilities, creating new opportunities for product-focused businesses.
Conclusion: Building Your PPC Success Foundation
Creating a successful PPC strategy isn’t about chasing the latest tactics or spending the most money. It consists of building a systematic approach that quickly drives the right traffic, at the right cost, with messages that resonate with your target audience.
For businesses seeking expert guidance, partnering with experienced agencies can accelerate results while avoiding common pitfalls. Straight North has a proven reputation of helping clients achieve remarkable outcomes. Reach out to Straight North if you want us to help you take your PPC strategy to the next level.








